Ask The Doc
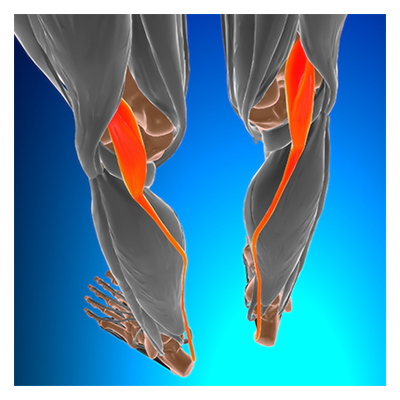
What is “Tennis Leg”?
Classically, the term was used to describe a plantaris rupture. The plantaris is a small muscle that starts in the back of the knee and runs under the gastrocnemius (large calf muscle) attaching the calcaneus (heel bone) just inside the Achilles tendon. It plays a small role in ankle plantar flexion. Injury to this muscle occurs with a hard dorsiflexion force (foot going up towards the shin) and a feeling/hearing of a pop can be associated.
More recently, this term can also be used to describe a medial gastrocnemius (big calf muscle) or soleus (calf muscle under the gastrocnemius) strain. These large muscles of the calf will not pop, but injuries can result in significant pain and dysfunction.
For pain in this area without an injury, you should contact a physician as this could be a deep vein thrombosis (blood clot of the leg).
Treatment for tennis leg is primarily focused on decreasing pain, stretching, and regaining strength. A walking boot can help to keep the ankle from pushing down which requires calf activation. Stretching the calf muscles, with the knee extended (plantaris and gastrocnemius) and the knee flexed (soleus). Compression, icing and anti-inflammatories may help decrease discomfort and swelling. There should be no pain with walking before considering running, jumping and more athletic maneuvers.